Cooling
PRODUCTS » DATA CENTERS » Cooling
Information
Hot / cold aisle
The standard practice in data centers is to arrange cabinets into hot / cold aisles. The cabinets are positioned facing each other, and cold air is supplied through perforated tiles in a raised double floor. According to the ANSI/TIA/EIA-942-A standard, the recommended width for a cold aisle is 1,2 meters, which typically corresponds to the size of two double floor tiles. Cold air is supplied via perforated tiles at the front of the cabinets, which is distributed to cabinet by fans. Cold air is supplied to active elements through doors with 80% perforation. In this configuration, the double floor is used to deliver the cold air, and it is necessary to cover all other openings in the floor, such as cable entries. The reason for this is to maintain static air pressure in the double floor and to minimize cold air loss.
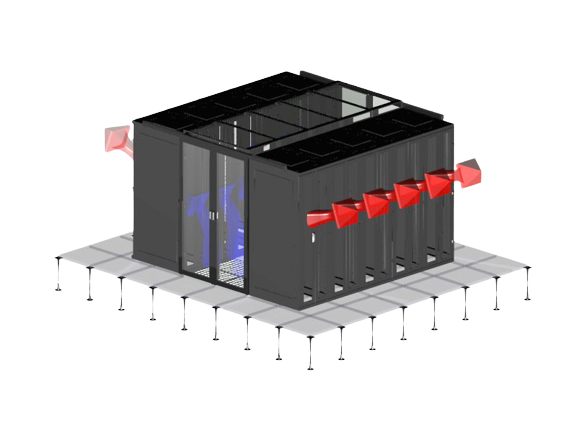
Contained cold aisle
The open hot / cold aisle configuration can have shortcomings in terms of recirculating heated air, leading to the risk of hot-spots or locally overheated areas. The solution is a contained cold aisle. This is a closed, modular, expandable system, which physically separates the cold air from the exhaust of hot air. It creates a separate area for hot and cold air and prevents them from mixing. Cool air is supplied to the closed aisle through perforated tiles in the raised floor or locally through side cooling units installed directly in line with the cabinets. The standard width of a contained cold aisle is typically 1,2 meters (two floor tiles) or 1,8 meters (three floor tiles). At the ends, the aisle also has a glass sliding door. The use of this solution is becoming standardised and is especially recommended for its cooling capacity and efficiency in achieving the lowest energy consumption of the data center.
Closed modular solution
A closed modular solution offers maximum energy efficiency and scalability, making it an ideal choice for the long-term development of a data center. This solution can be customized and tailored to meet the customers’ needs. It allows creation of different zones within a single room with different operating temperatures and with varying densities of thermal load. The solution is characterised by a high-IP cabinet. which protects the installed components against dust and moisture. Side cooling units are attached directly with the racks to make a closed module with an internal cold zone at the front part of the cabinet and hot zone at the rear of the cabinet. This solution allows you to combine any number of racks and cooling units in the module. Our specialists will prepare a proposal for the project to ensure the space capacity required for installation of the equipment and the corresponding power conditioning, including any needed redundancy.
Floor feed
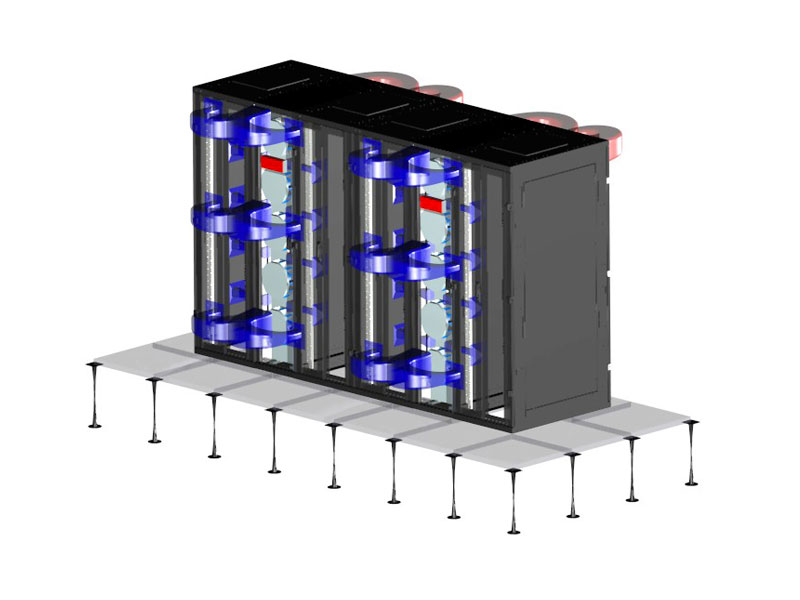
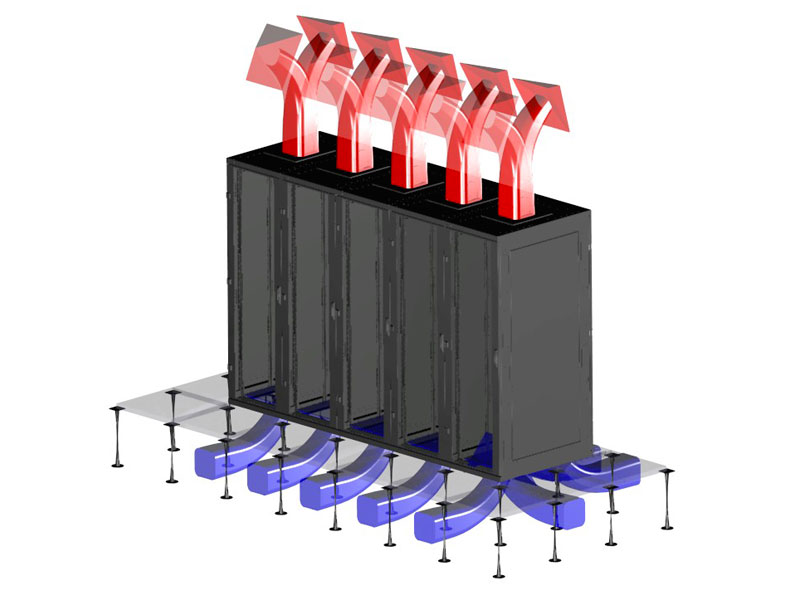
This method increases the efficiency of cold air delivery from the double floor to the installed equipment. The cabinet is installed over the opening in the double floor. A deflector, located at the bottom of the cabinet, directs cool air towards its front section. The cold air is then further directed within the front section of the cabinet using a door without perforations, which can be made of glass or metal. The hot air is extracted from the rack either by doors with 80 % perforation or the cabinet ceiling. By installing a cool air supply regulator at the bottom of the cabinet, the airflow may be adjusted or completely shut off the delivery when the cabinet is not in use. The advantage of this cooling method is great flexibility in planning of the room usage. It eliminates the need for separate cabinets in hot and cold aisles since the hot and cold air can be effectively separated within individual cabinets. To achieve this, it is necessary to install a separating frame inside the cabinets to strictly separate cold and hot air.
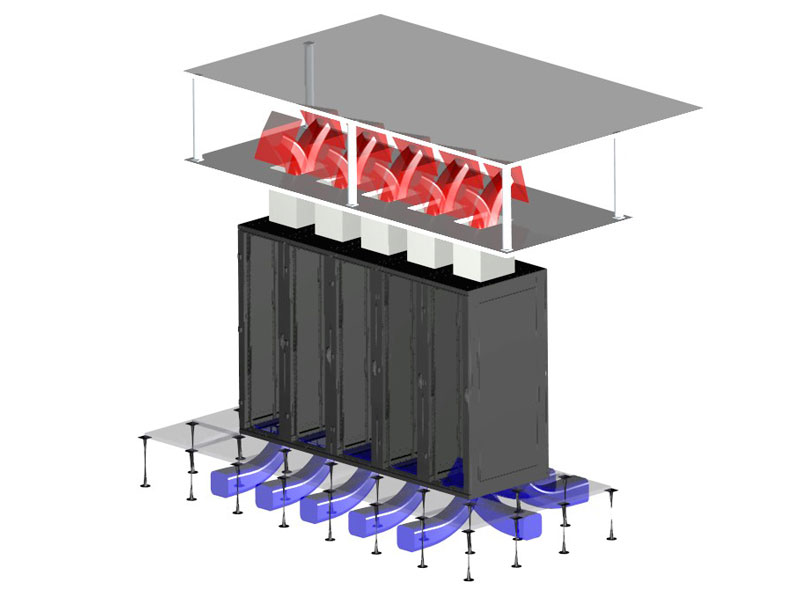
Floor feed with plenum return
A possible disadvantage of cold aisle and cooling supply from the floor and return to the room is that hot air is brought into the surroundings of the installed equipment. This does not cause an issue when it is addressed in the design stage. In certain cases, a possible solution is to completely separate the warm air in areas with high thermal loads due to the concentration of the installed equipment. The solution in such cases is to supply cooling air from the room or raised floors and return it to the ceiling instead of circulating it back into the main hall. The hot air is directed to the ceiling or a double ceiling. A rear deflector located in the upper part of the cabinet helps to optimise the flow of hot air into the outlet extension. A large adapter allows the passage of large quantities of air at a relatively low speed. A cold air intake is on the front door of the cabinet, and hot air is discharged through the outlet extensions to the ceiling / double ceiling above the devices. Air conditioning units take the hot air from the ceiling, cool it and deliver it back under the raised floor. The air cooling circuit is closed. This solution provides high efficiency cooling for very large volumes of hot air. Research indicates that this solution can be used to cool up to 30 kW per cabinet.
Our specialists will gladly help you choose the optimal solution for your needs. By selecting the right type of cabinet and accessories, you can save a significant amount of money on the operation of your equipment.